With technological advancements, internet antenna for home has become the go-to solution for accessing high-speed internet, especially in regions experiencing limited connectivity.
Interestingly, manufacturers are even designing internet antennas with signals that can penetrate obstacles.
This gives internet and WiFi reasons not to worry, as the WiFi signals get to them with steady signal strength.
In today’s article, we consider the types of internet antenna for home, the best practices, and shopping criteria.
Table of Contents
- What Is an Internet Antenna for Home?
- Types of Internet Antennas for Home
- Internet Antenna for Home Best Practices
- Shopping Criteria for Internet Antenna for Home
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What Is an Internet Antenna for Home?
We otherwise refer to it as a wireless or WiFi antenna, which is a device that receives/transmits wireless internet signals.
Generally, having this device in your home network means accessing the internet wirelessly via smartphones or computers.
We usually use wireless antennas to improve signal strength and extend WiFi access in areas with poor network coverage.
Moreover, they are available in different options, including indoor antennas that you can incorporate into WiFi routers and external antennas that you can mount on your roof.
Types of Internet Antennas for Home
We categorize wireless antennas into omnidirectional and directional antennas.
Omnidirectional Antennas

(A dipole antenna symbol)
These antennas offer the widest coverage, radiating signals at 360-degree angles. However, this wide coverage reduces the antenna range.
Funny enough, you can use these antennas in indoor or outdoor environments.
Generally, we have the following omnidirectional antenna types:
- Outdoor Omni Antennas: We use these antennas to improve the signal in outdoor settings by connecting them to points and routers.
- Ceiling dome antennas: As the name suggests, we install them on the home’s ceiling and then link them to the access point or WiFi router using a coaxial cable.
- Dipole/rubber duck antenna: These antennas have two equal conductive elements, one acting as a receiver and the other as a transmitter. They are common on WiFi USB adapters and access points.
Directional Antennas
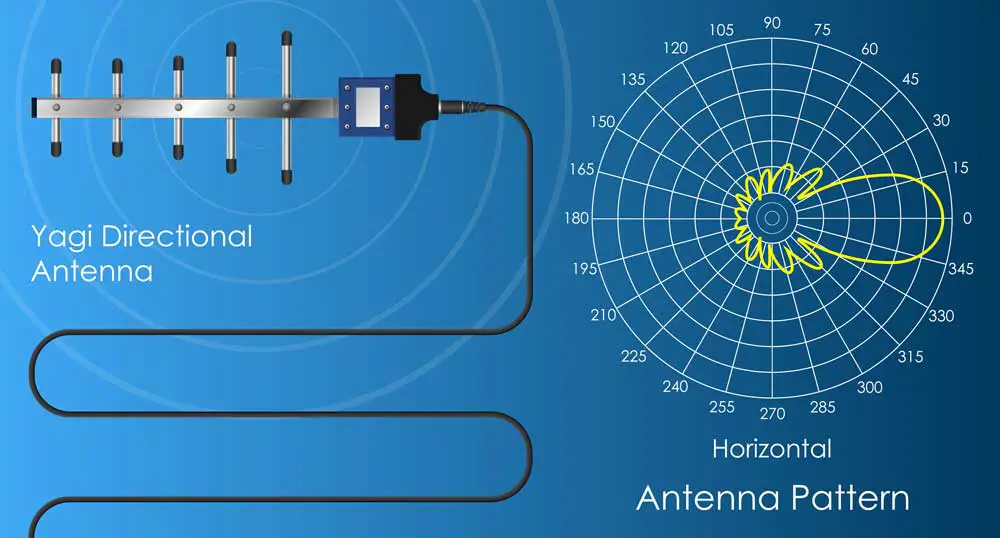
(A directional Yagi antenna)
These antennas focus all their signals in a single direction, just like a flashlight would if you power it on.
This makes them receive or transmit signals from far but with smaller coverage.
Therefore, directional antennas work well for long-range point-to-point networks, especially for bridging an internet connection between two buildings.
Below are some common types of directional antennas:
- Yagi antennas: The antenna is the most common directional option, with an arrow-like shape pointing in the direction of transmission or reception. Usually, a Yagi antenna will radiate about 45 degrees.
- Mini panel antenna: These are low-profile antennas we use for sending and receiving signals, with a common application in indoor WiFi signals. Unlike the Yagi antenna, which offers a radiation pattern of 45 degrees, this option provides about 60 degrees. But, like the Yagi antenna, you must point it in the transmission and reception direction to achieve optimal reception.
- Panel antenna: Although these antennas have a radiation pattern of 35 degrees, they offer a better directionality than mini panel antennas. Therefore, you can use them on a WiFi adapter to receive data from far or connect them to a router to send data far.
- Parabolic grid antenna: Parabolic antennas are extremely directional and have an ultra-high gain. Generally, they contain a narrow beam width of about 3-20 degrees. Their unique design gives them the ability to work in extreme conditions. Moreover, since they can transmit/receive signals from far, they work effectively as point-to-point WiFi network devices.
- CPE antennas: Customer Premise Equipment (CPE) antennas can fall under parabolic or panel antennas. Generally, CPE antennas can receive signals from as far as 12 miles.
Internet Antenna for Home Best Practices

(A home modem)
Wireless antennas function effectively when they experience blockage or obstruction from objects or physical structures.
Here are internet antenna best practices to improve performance:
Antenna Placement
For an antenna, especially the directional option, alignment/orientation and placement is everything.
When the antenna receives signals, you should align it to face the direction of the transmitting tower without any obstacles.
Moreover, when the antenna is transmitting signals, position it centrally in your home to distribute the signals evenly.
Choose The Right Antenna
Although this sounds as simple as walking into a shop and out with a functional antenna, it is not always the case.
Generally, you must evaluate your needs and application case before buying an antenna.
For instance, while a directional antenna works well for long-range applications and targeting specific locations, the omnidirectional antenna will serve you well for general home use.
Employ High-quality Coaxial Cable
Using a high-quality coaxial cable with proper shielding helps to minimize signal interference and loss.
Moreover, the cable should be short to preserve the signal strength.
Regular Maintenance
From time to time, inspect your antenna or coaxial cable for signs of damage and make the relevant repairs.
If you notice any damage, however small, move quickly to make a replacement or repair.
Moreover, ensure the area around the antenna is clean and free from any obstruction that might affect signal reception.
Shopping Criteria for Internet Antenna for Home

(An antenna on the rooftop)
Buying a home internet antenna is not a walk in the park and calls for some serious considerations.
Here are a few shopping criteria to consider.
Antenna Type
By now, you would know that not all antennas will work well to meet your needs since antennas are designed for a specific purpose and situation.
For example, a standard internal or omnidirectional antenna works perfectly for covering the whole house.
Conversely, a directional option like the Yagi antenna will serve you well if you want to meet access in specific areas.
Frequency Compatibility
The antenna frequency should be compatible with your WiFi network.
Generally, most WiFi networks work on the 2.4 or 5 GHz bands, and purchasing an antenna that functions in the same bands would be wise.
Gain
The gain represents the antenna’s ability to amplify and focus signals in a specific direction.
Generally, devices with a higher gain offer a long-range and stronger signal but with a narrow coverage angle.
Therefore, by evaluating your requirements, buying an antenna with the right gain will be easy.
Outdoor vs. Indoor Antenna
Determine whether you need an indoor or outdoor antenna early during installation.
Although outdoor antennas provide a more extended range and higher gain, they must come with weather-resistant features for increased performance and lifespan.
Device Compatibility
Check the available devices like access points and routers and purchase an antenna compatible with their features.
The most important things to consider are the N-type and RP-SMA standard connectors.
Signal Amplification
Manufacturers understand that sometimes the signals might be poor and have developed antennas with boosters and amplifiers.
Such antennas can transform weak signals into strong signals to yield a strong internet connection.
Budget and Reviews
Start by setting a budget for your antenna and only commit to buying within that budget.
However, never settle for a poor-quality product because it fits your budget but rather find a good compromise between price and quality.
Moreover, evaluate the ratings and reviews from different customers to understand how reliable an antenna is.
You will get good performance if you choose 5-star rated antennas with positive customer reviews.
FAQs
What does an antenna do for the internet?
An antenna is a wireless device that transmits or receives signals enabling WiFi-based devices to have reliable access to the internet.
Therefore, the antenna eliminates the need for cable internet, but you must connect it to an access point or router to work effectively.
In such a case, the antenna captures data and converts it into electromagnetic signals for broadcasting to the intended area.
What does it mean for an internet antenna to work in a dual-band?
An antenna works in a dual-band if it can operate simultaneously on two frequency bands.
For example, most dual-band antennas supporting WiFi networks operates under the 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency bands.
This means a dual-band antenna can transmit or receive signals on any of the two bands.
However, while the 5 GHz bands offer a short range and higher data speeds, the 2.4 GHz option supports a long range with the ability to penetrate obstacles.
Conclusion
Wireless antennas are slowly taking over the industry, mainly because they help boost the WiFi signal.
However, to get the best out of your home internet antenna, you should position it appropriately, implement regular maintenance, and buy a reliable antenna & coaxial cable.
The above shopping criteria can provide a clear blueprint for choosing an appropriate wireless antenna.
Feel free to contact us if something feels off and needs clarification.
